Traffic routing methods
Azure Traffic Manager supports six traffic-routing methods to determine how to route network traffic to the various service endpoints. For any profile, Traffic Manager applies the traffic-routing method associated to it to each DNS query it receives. The traffic-routing method determines which endpoint is returned in the DNS response.
The following traffic routing methods are available in Traffic Manager:
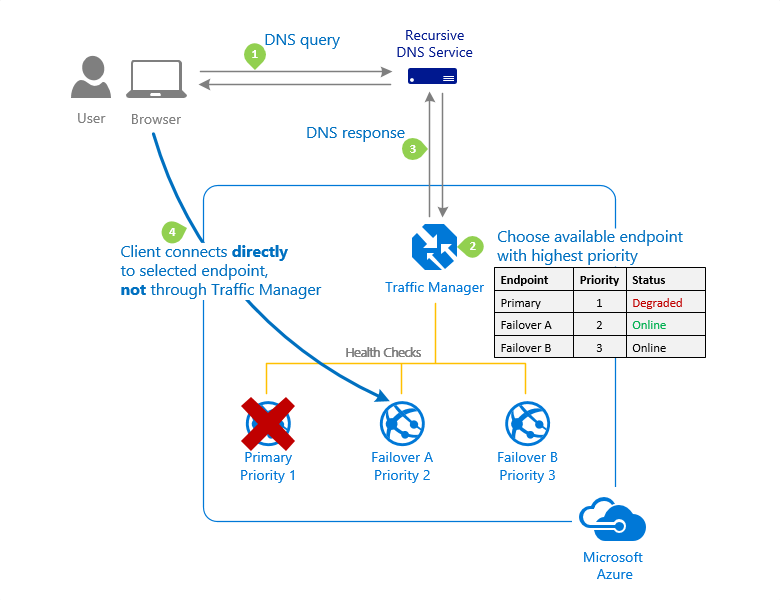
Priority routing method
Priority
- Select this routing method when you want to have a primary service endpoint for all traffic.
- You can provide multiple backup endpoints in case the primary or one of the backup endpoints is unavailable.
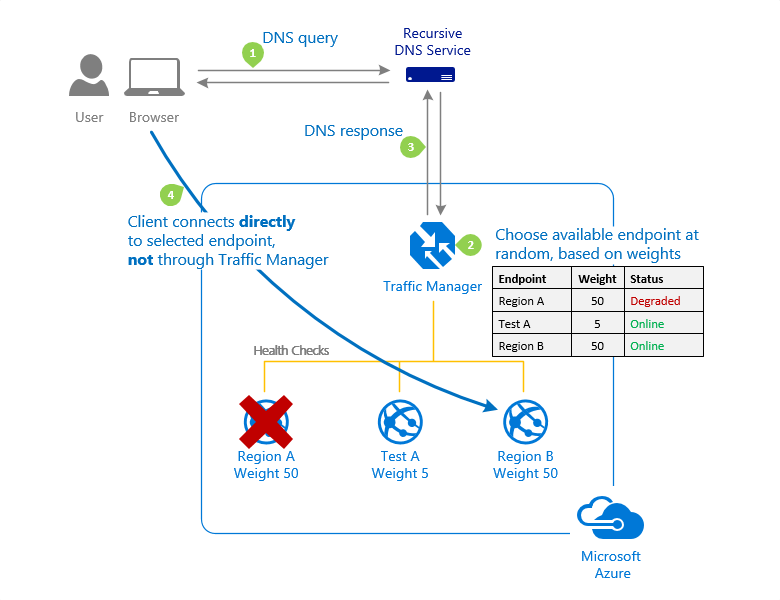
Weighted routing method
Weighted
- Select this routing method when you want to distribute traffic across a set of endpoints based on their weight.
- Set the weight the same to distribute evenly across all endpoints.
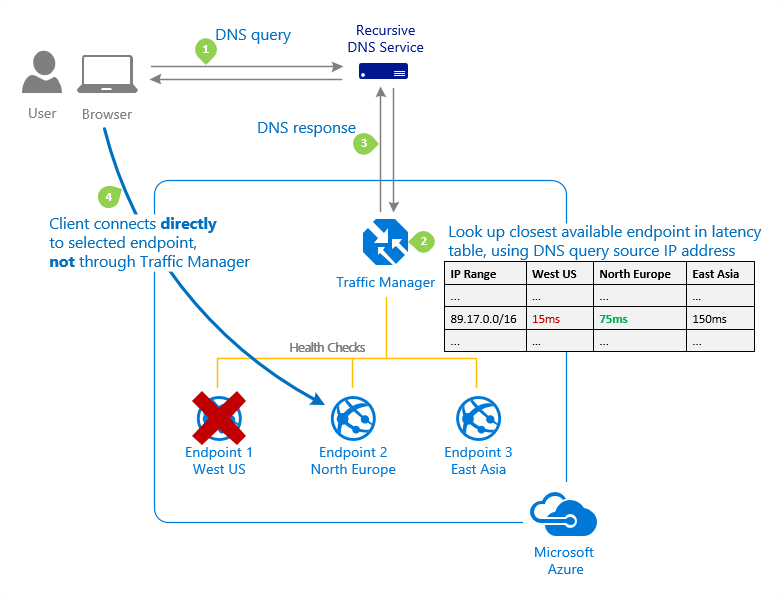
Performance routing method
Performance
- Select the routing method when you have endpoints in different geographic locations, and you want end users to use the "closest" endpoint for the lowest network latency.
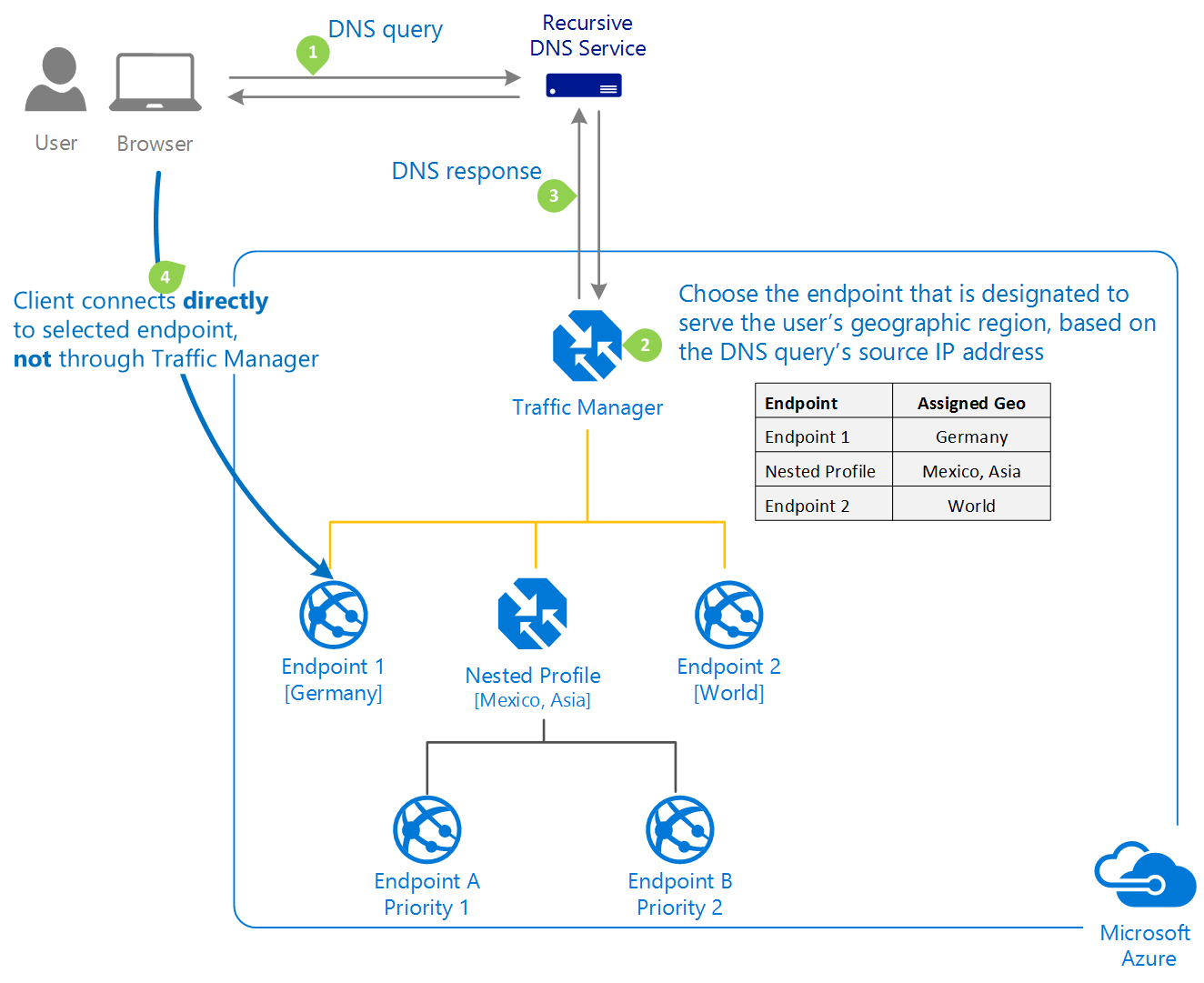
Geographic routing method
Geographic
- Select this routing method to direct users to specific endpoints (Azure, External, or Nested) based on where their DNS queries originate from geographically.
- With this routing method, it enables you to be compliant with scenarios such as data sovereignty mandates, localization of content & user experience and measuring traffic from different regions.
MultiValue routing method
MultiValue
- Select this routing method for Traffic Manager profiles that can only have IPv4/IPv6 addresses as endpoints.
- When a query is received for this profile, all healthy endpoints are returned.
Subnet routing method
Subnet
- Select this routing method to map sets of end-user IP address ranges to a specific endpoint.
- When a request is received, the endpoint returned will be the one mapped for that request’s source IP address.
 1500bytes
1500bytes